Condition Builder
Step conditions enable you to control the flow of your workflow on a per-step basis. By associating one or more conditions with any step, Engagespot evaluates these conditions during each workflow run to decide if the step should be executed. For example, you might send an email only if the preceding in-app notification has not been read or seen.
Conditions Editor
The Engagespot Console includes a conditions editor that provides helpful abstractions on top of the data model. This means you don't need to remember how to format variables or name operators; Engagespot makes the appropriate options available to you.
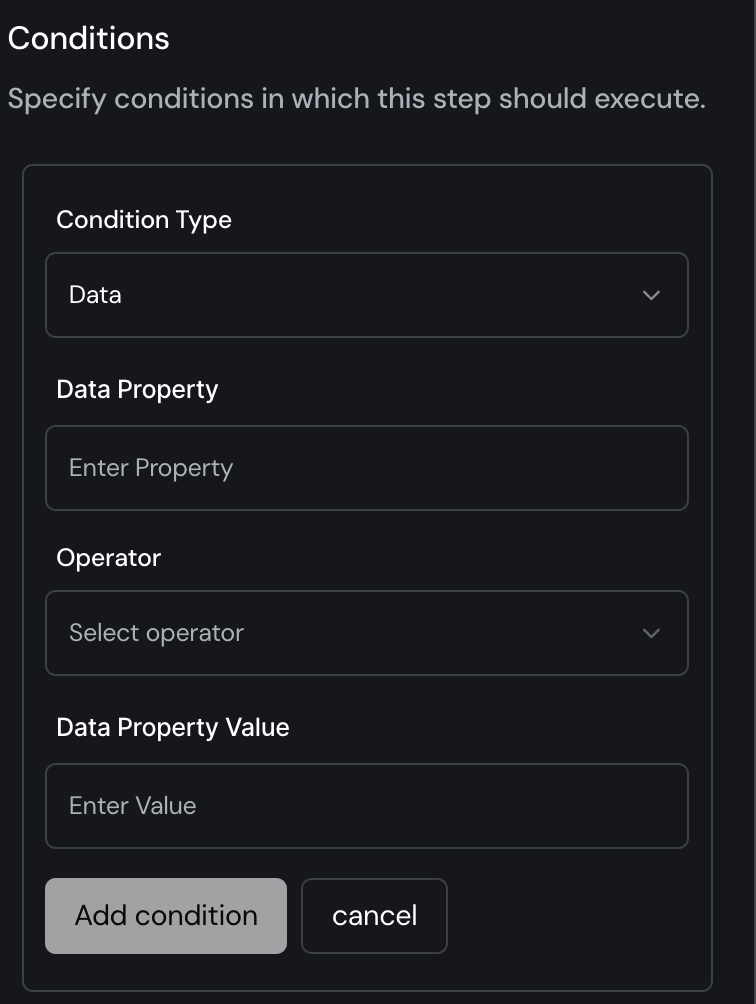
When you click "Add condition," you will see the following fields to specify conditions for step execution:
- Condition Type: Choose the type of condition, such as Data, Step, or Recipient.
- Previous Step: Choose the reference to the previous step (only in the case of Step condition type).
- Data Property: Enter the specific data property to be evaluated.
- Operator: Select the operator to apply, such as "is equal to" or "greater than."
- Data Property Value: Enter the value to compare against the data property.
- Data Key: Enter the specific key of data (only in the case of Fetch Step).
You can also use the conditions editor to combine multiple conditions together via either 'AND' or 'OR' operators.
AND combined conditions require all conditions to be true for the evaluation to pass.
OR combined conditions require at least one condition to be true for the evaluation to pass.
Advanced Condition Builder
Modeling a Condition
In Engagespot each condition is a combination of three properties: a contextual variable, an operator, and an argument.
Example:
data.step.sms_1.state == 'success'
Components of a Condition
-
Contextual Variable: This variable is formatted as a string in the following manner:
<conditionType>.<path>. The conditionType determines the type of condition, while thepathspecifies where to look up the data for evaluation. In our example:data.step.sms_1.statedata: Represents the condition type, indicating that this condition pertains to data within the workflow.step.sms_1.state: Specifies the exact path within the data object, pointing to the state of thesms_1step.
-
Operator: This is the comparison operator used to evaluate the condition. In our example:
==: This operator checks for equality between the state of thesms_1step and the specified argument.
-
Argument: This is the value against which the contextual variable is compared. In our example:
'success': This argument represents the expected state of thesms_1step.
Condition Types
The shared conditions model supports the following types of conditions:
-
Data: Evaluates against a property in the workflow trigger data payload. This condition type is useful for checking specific data points that initiated the workflow, such as user actions or external system inputs.
-
Recipient: Evaluates against a property of the workflow run recipient. This can be used to tailor workflow steps based on recipient attributes like user roles, subscription status, or custom profile fields. For example, you might send a different message to users based on their subscription level or account status.
-
Step: Evaluates against a property of the currently executing workflow step. This type of condition is used when the decision depends on the outcome or data from a specific step in the workflow. For instance, if a previous step involved fetching data from an API, the condition might check if the fetched data meets certain criteria before proceeding.
Contextual Variable
Engagespot uses contextual variable formatted as strings in the following manner:<conditionType>.<path>.
The conditionType of the variable determines the condition type, while the path specifies where to look up the data for evaluation.
The allowed variable formats in Engagespot are as follows:
| Contextual Variables | Data Type | Description | Example | Applies For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
data.step.<step_ref>.data | String | Evaluates the string input from a WaitForInput Step | data.step.waitForInput_1.data === 'Y' | Wait For Input |
data.step.<step_ref>.data.<path> | Object | Evaluates the object output from a Fetch Step | data.step.fetch_1.data.status === '200' | Fetch Step |
data.step.<step_ref>.state | State | State of a workflow step | data.step.sms_1.state == 'success' | Any Step |
data.step.<step_ref>.message.<message_status> | MessageStatus | Evaluates the message status for a channel step | data.step.email_1.message.read === true | Channel Step |
data.recipient.<prop> | Object | Evaluates against a property on the workflow recipient | data.recipient.age > '20' | Any Step |
data.data.<path> | Object | Evaluates against a property in the workflow data | Any Step |
Operators
You can use any of the following operators in condition comparisons:
Comparison Operators in EngageSpot
| Name | Operator | Description |
|---|---|---|
equal to | == | Checks if two values are equal. |
not equal to | != | Checks if two values are not equal. |
greater than | > | Checks if the left value is greater than the right value. |
greater than or equal to | >= | Checks if the left value is greater than or equal to the right value. |
less than | < | Checks if the left value is less than the right value. |
less than or equal to | <= | Checks if the left value is less than or equal to the right value. |
Arguments
Engagespot utilizes the condition argument to assess conditions based on expected values. These arguments can be categorized as either static or dynamic properties.
Static Arguments
Static arguments can include the following JSON literals:
- Strings:
"foo","bar","baz" - Numbers:
1.0,2,10000 - Booleans:
true,false null
Dynamic Arguments
Dynamic arguments function similarly to contextual variables. Engagespot requires these arguments to be formatted as a string in the form of <conditionType>.<path>. This format allows Engagespot to derive a value from runtime data properties. You can use all the contextual variables as previously discussed.
State Options
The state Options represents various states a workflow step can have. Here are the possible states:
| State | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| scheduled | scheduled | The step is scheduled for execution. |
| queued | queued | The step is in the queue awaiting execution. |
| running | running | The step is currently being executed. |
| success | success | The step has completed successfully. |
| failed | failed | The step has failed. |
| skipped | skipped | The step was skipped. |
| batched | batched | The step is part of a batch execution. |
Message Status
The MessageStatus represents various statuses a message can have during its lifecycle. The statuses differ based on the channel through which the message is sent. Here are the possible statuses for each channel:
| Channel | Statuses | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sms | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for SMS messages. |
| inapp | delivered, sent, seen, read, interacted, not_sent | Delivery and engagement statuses for in-app messages. |
delivered, delivery_attempted, sent, seen, read, interacted, not_sent | Delivery and engagement statuses for email messages. | |
| slack | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for Slack messages. |
| discord | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for Discord messages. |
| webhook | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for Webhook messages. |
| mobilePush | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for mobile push notifications. |
| webPush | delivered, sent, not_sent | Delivery statuses for web push notifications. |
delivered, delivery_attempted, sent, not_sent, read, replied | Delivery and engagement statuses for WhatsApp messages. |
Combining Conditions
The conditions editor allows for complex logic by combining multiple conditions using 'AND' and 'OR' operators:
-
'AND' Conditions: All conditions must be true for the evaluation to pass. This is useful when you need to ensure multiple criteria are met before proceeding. For example, you might require that a user is both subscribed to a specific service and has interacted with a previous message.
-
'OR' Conditions: At least one condition must be true for the evaluation to pass. This is useful for more flexible criteria where any one of several conditions being true is sufficient. For example, you might proceed if a user either seen a message in inApp or Updated his preference.
Example of Combining Conditions
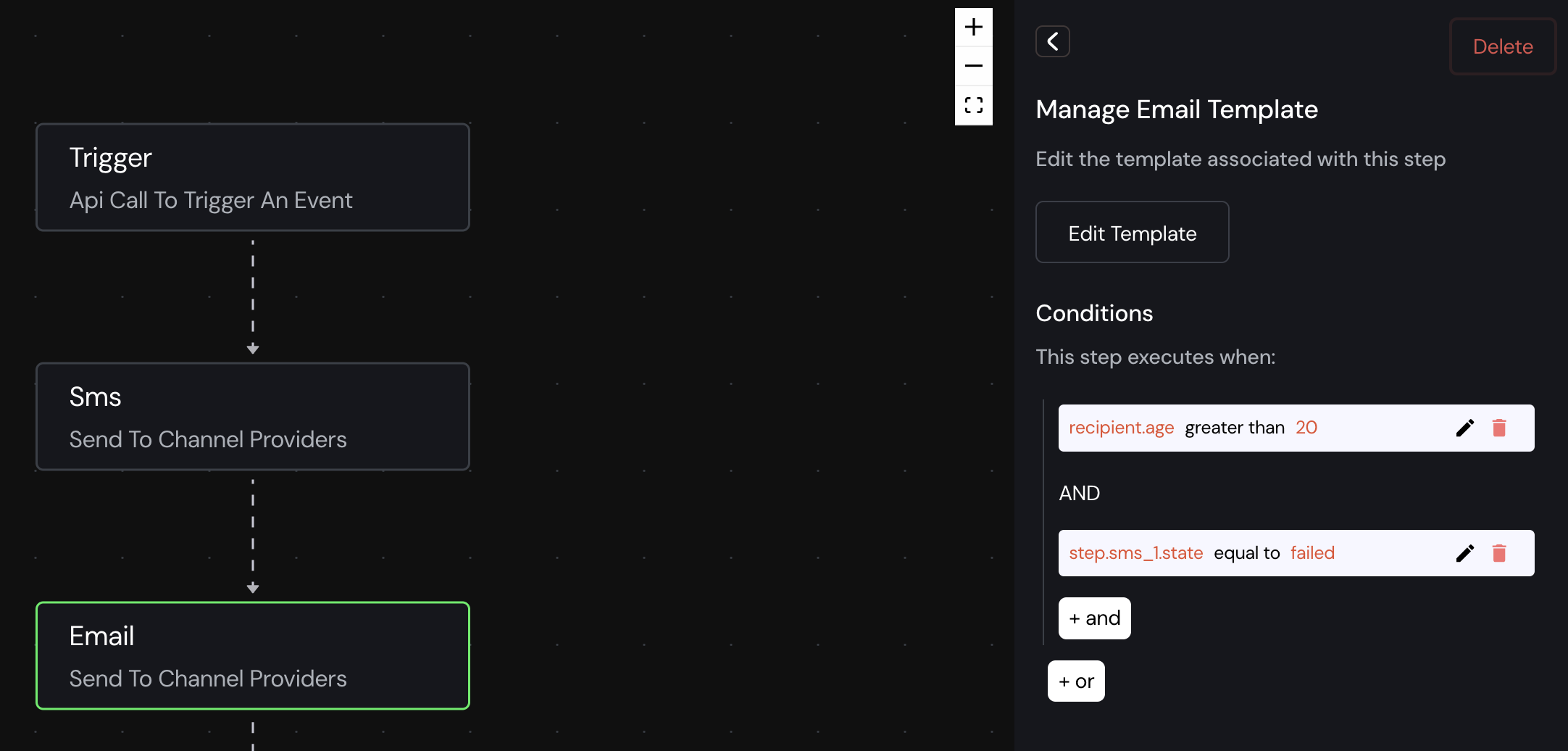
In the above example the email step is only executed only if the recipient's age is greater than 20 and the sms step must be failed.